There are various ways to appear in Google search results, but the first step is always the same: indexing. This means being included in the index that Google uses to build its SERPs (Search Result Pages).
In this article, you will learn how to index your page on Google, why it’s essential, how to fix common indexing errors, and which tools to use to improve the process.
Ready? Scroll down to keep reading.
What Does It Mean to Index a Web Page on Google?
How many pages are there on the web? Billions? Hundreds of billions? Hundreds of thousands of billions? There are too many, in any case: more than the most powerful search engine could crawl in just a few seconds to respond to a query. At least, without some help.
If we have Google to search for information, Google has its index. In it, Google stores and organizes data about the content of those hundreds of billions of URLs across the web. This allows it to quickly identify which pages answer each query and determine which should appear at the top of the SERPs.
When a URL is crawled, classified, and evaluated within Google’s database, it is said to be indexed. Google automatically indexes these pages as it crawls the web with its crawlers (the famous “spiders”).
However, this process takes a long time when left up to Google (or to fate, if you prefer). Therefore, if you want your page to appear in Google search results, the best approach is to request indexing manually.
Why Is It Important for Your Page to Be Indexed?
One of our clients came to us feeling like the invisible man: his site had been live for months and only received traffic through social media. He even searched for his site name on Google but couldn’t find it until several SERPs later.
The surprise wasn’t big when we discovered that only a couple of his pages were indexed. After all, indexing and visibility go hand in hand. This is because, once a page is indexed, it becomes part of Google’s database… and Google only uses the data it stores in its index to build its SERPs.
Why? Because crawling URLs in real-time to respond to queries would be highly inefficient. As the most widely used search engine globally (capturing 92% of computer searches in January 2024), not being in its index means truly being invisible on the web.
The more of your URLs that appear in that index, the more chances you have of ranking for various keywords and generating new customers… Especially if you implement a solid and quality SEO strategy that helps you rank well in the SERPs.
Thus, indexing your website’s pages directly impacts your chances of receiving traffic. And not just any traffic, but organic traffic — users who find your site through searches related to your offerings or brand. These users are already somewhat interested in what you offer.
Steps to Index a Page on Google
As we saw above, there are multiple ways to get your page into Google’s index. First of all, you can always wait for Google to take the initiative and, after months of crawling the web, finally arrive at your site.
But waiting is out of fashion — who has time for that? Nowadays, you need quick solutions. So, let’s see how to index a page on Google manually.
Use Google Search Console to Request Indexing
Indexing a web page has a prerequisite: create a Search Console account linked to your website. Once you have it, select the domain you’re working with. Next, insert the URL you want to index into the search bar at the top of the page and press “Enter.”
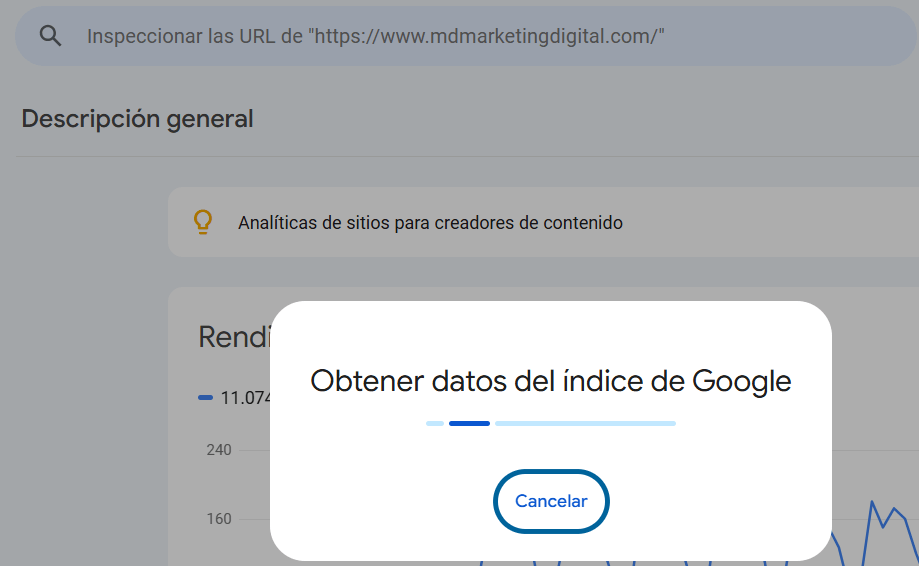
This will prompt Search Console to inspect the address. It shouldn’t take more than a few minutes. Once done, the page will show a notification, letting you know if the entered address is indexed or not.
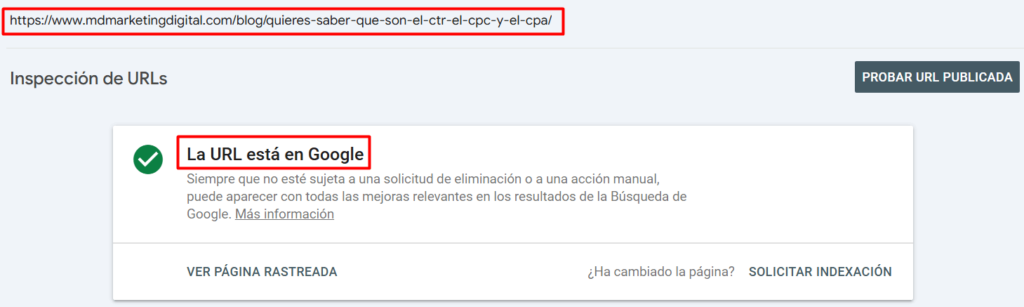
If the URL isn’t indexed, the option to request indexing will appear:
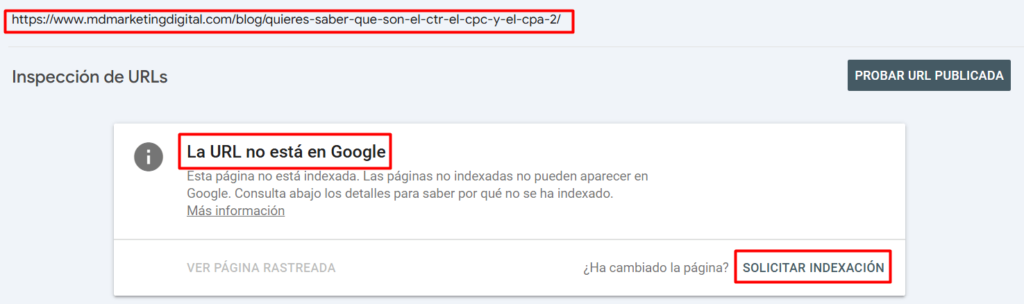
Clicking it will send the request to the system. To avoid complications, we recommend clicking “Test Live URL” first. This will help you verify if Google deems the page suitable for indexing.
Next, it’s time to wait. How long? Between less than a day and more than a week, depending on the characteristics of the webpage to be indexed. But we’ll delve into this in more detail a few sections later.
Submit Your Website’s Sitemap to Google
In cases like our client’s, indexing page by page can be quite tedious (to say the least). To optimize resources, we decided to submit the site via a sitemap.
A sitemap is a file that contains the URLs of a website, indicating their type of content, when they were updated, and their relationships with one another, among other details.
It helps optimize indexing. Not only because it sends all URLs to be indexed at once but because it “guides” Google through your site, making it easier for it to access the information.
Additionally, it highlights which pages should be prioritized and which to ignore. It also prevents any pages from being left unindexed.There are three ways to create a sitemap: manually, with online tools, and using plugins. In this article on sitemaps, we explain step-by-step how to create them. Take a quick read and come back to continue with this guide!
When the sitemap is ready, you must upload it to Google Search Console. This is done by selecting the “Add Property” option. After clicking, choose the “Sitemaps” option and paste your domain’s URL with the sitemap added to the root.
Next, click “Submit.” Google will start processing the site and crawling it page by page. Search Console will show you the status of the sitemap and notify you of any issues with URLs.
Other Methods to Force Indexing on Google
Beyond requesting indexing in Search Console, there are other ways to speed up the process. For example:
- Backlinks and internal links: Having links from other sites to yours helps Google crawl them, as well as links that connect your pages. Especially if they’re on high-quality sites related to yours. A good link-building strategy will also help improve your SERP rankings.
- Tools and programs: Another way to speed up the crawling process is to use specific plugins or tools. Rank Math, for example, is often used to index WordPress sites. It not only creates sitemaps automatically but also allows you to request indexing from within WordPress.
- Constant updates: Publishing new content regularly or optimizing your pages can help Google consistently crawl your site. This is because, when it detects that the content is regularly updated, Google increases the crawl rate of your site to ensure it offers fresh content to its users.
- Social media content: High engagement on social media can drive interaction with your website. As a result, Google will mark your site as “relevant” to users, helping its crawlers index it faster.
How Long Does It Take Google to Index a Page?
Indexing a page on Google takes time. In the best-case scenario, it’s just a few hours. In the worst, several weeks (or more). What does it depend on? Not a ‘perspective’ but a set of factors that determine the priority Google gives to your site when crawling it. What are these factors? Let’s take a look:
Factors Influencing Indexing Speed
Broadly speaking, the key factors determining how fast a webpage gets indexed are:
- Site authority: This is the most influential factor in determining indexing speed and crawl frequency. It depends on the quality and number of backlinks, the site’s relevance to a topic, and the trust Google has developed over time.
- Content quality: Producing high-quality content (relevant, unique, precise, and user-friendly) is a direct ticket into Google’s index. Since Google believes these pages are more likely to satisfy users’ needs, it tends to prioritize indexing them.
- Update frequency: For Google, frequent updates are an indicator of quality content. Constantly publishing content helps Google detect your site faster and index it more regularly.
- Loading speed and responsive design: Another factor that helps Google prioritize a page is having an optimized design. This is because Google believes it will better meet users’ search needs. The design optimization is determined by its loading speed and mobile-friendliness.
- Site size: Indexing a large site or many URLs simultaneously will take longer than indexing one or two pages. This doesn’t mean the URLs take longer to crawl but that they will be indexed gradually.
How to Know If Google Indexed Your Page
Worried that your site isn’t indexed? Requested Google to index a web page and want to know if it has already done so? Can’t find a URL in search results and need to check for indexing issues?
There are two ways to verify this:
- Google Search Console: The process for checking if a site is indexed using Search Console is similar to requesting indexing. Simply paste the URL you want to verify into the URL inspection bar and press “Enter.” Shortly after, you’ll receive the page status notification.
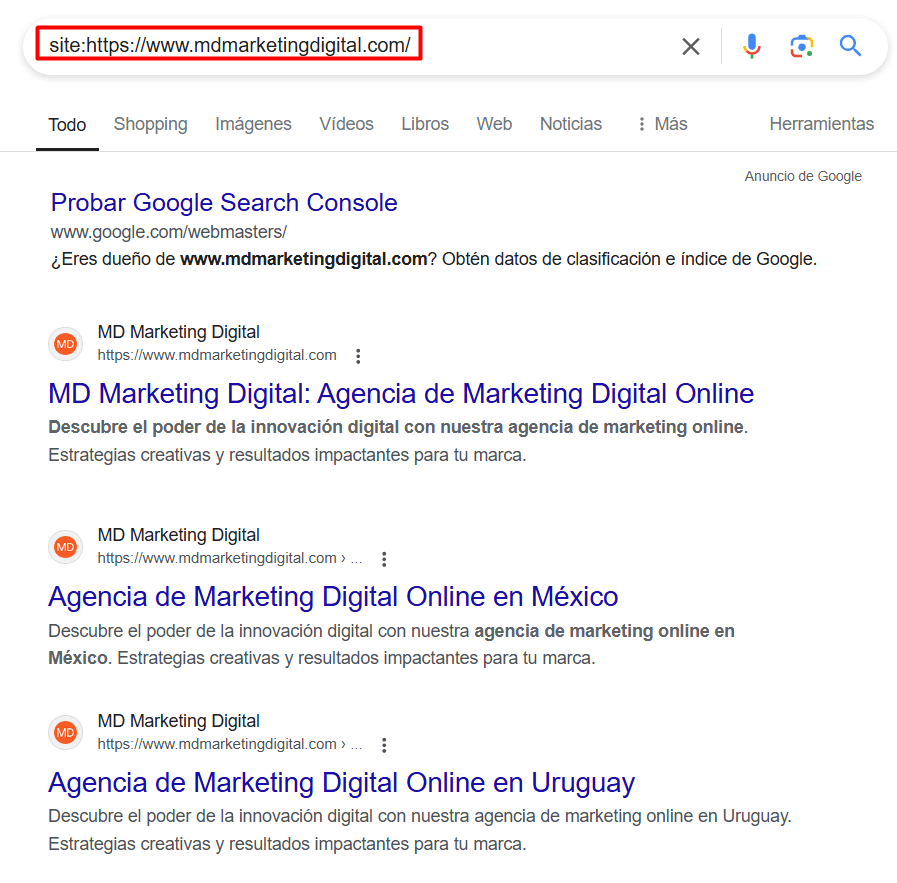
- Site Command: To know exactly how many of your site’s pages are indexed and find them all in the search engine, you can use the site command. Just enter site
.com into the search bar. The results will show you the number of URLs Google has stored for that site, as seen in the image below.
Common Errors That Affect Google Indexing
When we investigated our client’s site in more detail, we found some pages with errors that prevented their indexing. These are errors we’ve all experienced at some point because they’re quite common. For example:
- Robots.txt file issues: This file is used to indicate to search engines which pages to crawl and which to ignore. However, when it’s incorrectly configured, it can end up blocking key pages or even the entire site. On the other hand, the lack of a robots.txt file complicates crawling since the crawler doesn’t have directives to follow. The same applies to sitemaps.
- Multiple redirects or 404 errors: Redirects to non-existent pages (404) and multiple redirects confuse search engines. This not only makes indexing difficult but also negatively affects your ranking in the SERPs when indexing is successful.
- Duplicate content: That is, pages with similar content and keywords but different URLs. If canonical tags or redirects are not used, Google’s crawler won’t know which version to index, which prevents indexing.
- Noindex tags: As the name suggests, these tags prevent indexing. They’re used to temporarily hide test pages or URLs that don’t add value to the site’s ranking. When their use isn’t strategic, it’s considered an error.
- Loading issues: A page that takes too long to load may not be fully crawled by Google. Server errors (such as 500 codes) can block the crawler’s access to the page, causing incomplete indexing.
All of these can be discovered using the “Index Status” section in Search Console. This provides information that helps you correct some errors preventing indexing.
How to Fix Indexing Problems
It would be impolite to mention the most common indexing errors without explaining how to fix them. The solution our client found was to reach out to us, but maybe you’d prefer a different route. If so, we recommend that:
- For issues with robots.txt, access the file at yoursite.com/robots.txt. Check that it follows the directives and isn’t blocking any important pages.
- When dealing with redirects that prevent indexing, the first step is to check their status. You can use tools like Redirect checker or Ahrefs for this. Then, make sure they lead to existing pages and remove redirect chains.
- In cases of duplicate content, adding the tag <link rel=”canonical” href=”URL-of-preferred-page”> to the duplicate URL avoids indexing conflicts.
- To find noindex tags, first review the source code of each page. If it includes the tag <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”> and it’s a page that should be indexed, remove or change it to “index.”
- If your site has loading issues, you can use tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights. This allows you to analyze load speed and improve it. Investing in optimized design helps prevent these errors. Fixing 500-type error codes also ensures complete indexing.
Tools to Improve Your Page’s Indexing on Google
Whether you’re a professional in training or a DIY enthusiast, knowing which tools can make your life easier when indexing a page on Google is always useful. Here are some of the most effective ones:
- Google Search Console: It’s the Swiss army knife of SEO tools for website owners. Not only is it essential for indexing a page, but it also allows you to monitor and optimize its performance. Additionally, it provides performance reports and notifies you of indexing and visibility issues.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: This is a desktop program for SEO audits. Its functions include crawling a site’s URLs to find broken links, duplicate content, and redirects, and creating sitemaps, among other tasks. It helps you track your site’s structure and content, improving its indexability.
- SEMrush: A key tool for developing digital marketing campaigns. Besides conducting SEO audits to identify indexing and ranking issues, it also offers content and ad analysis functions.
- Ahrefs: With this program, you can audit your website from start to finish. This allows you to discover errors like duplicate content or non-existent URLs and optimize your site accordingly. Its features include keyword research, backlink tracking, and other tools to help enhance your SEO strategies.
Your Page on Google with One Click
Reality has surpassed fiction: instead of one invisible man, there are hundreds of thousands of websites that Google users cannot see. Indexing your pages on Google ensures you won’t be one of them.
Even though it’s a process that takes time, indexing a site is relatively simple. Having the right tools and knowing how to solve potential issues makes it even easier.
Will you try it on your website? Have you done it before? Tell us about your experience in the comments. We’re eager to read your story!
Of course, indexing pages on Google requires patience. And to have patience, you need time… and that’s something in short supply these days.
Does the idea of sitting down to audit your website, reviewing URL by URL, and waiting for them to be indexed make your schedule scream for help? We can assist with that.
At MD Marketing Digital, we’re a team of professionals specialized in… Can you guess? Rely on us to boost your web presence through solid strategies aimed at maximizing the benefits of online marketing. Having an indexed page is just the first step!Your website’s presence on Google starts with one click. Make sure it’s worth it.
- Best Email Marketing Agencies in Argentina: MD Ranking - April 14, 2025
- Top 10 Best Web Design and Development Agencies in Argentina - April 7, 2025
- MD Marketing Digital Ranking Research Methodology - February 7, 2025
¿Qué te pareció este artículo?
What do you think about this post?